Building a multi-channel support service for Globex customers - Intro
In this module you will participate to complete the implementation of a multi-channel support service for Globex customers that will enable clients to chat in real time with a team of agents.
Business and Technical Context
As an added initiative to the digital transformation, Globex wants to implement a new, all digital, support service where customers can get instant help from a team of support agents. The goal is to build a pluggable event-driven architecture that allows multiple communication channels and services to integrate with ease to the platform.
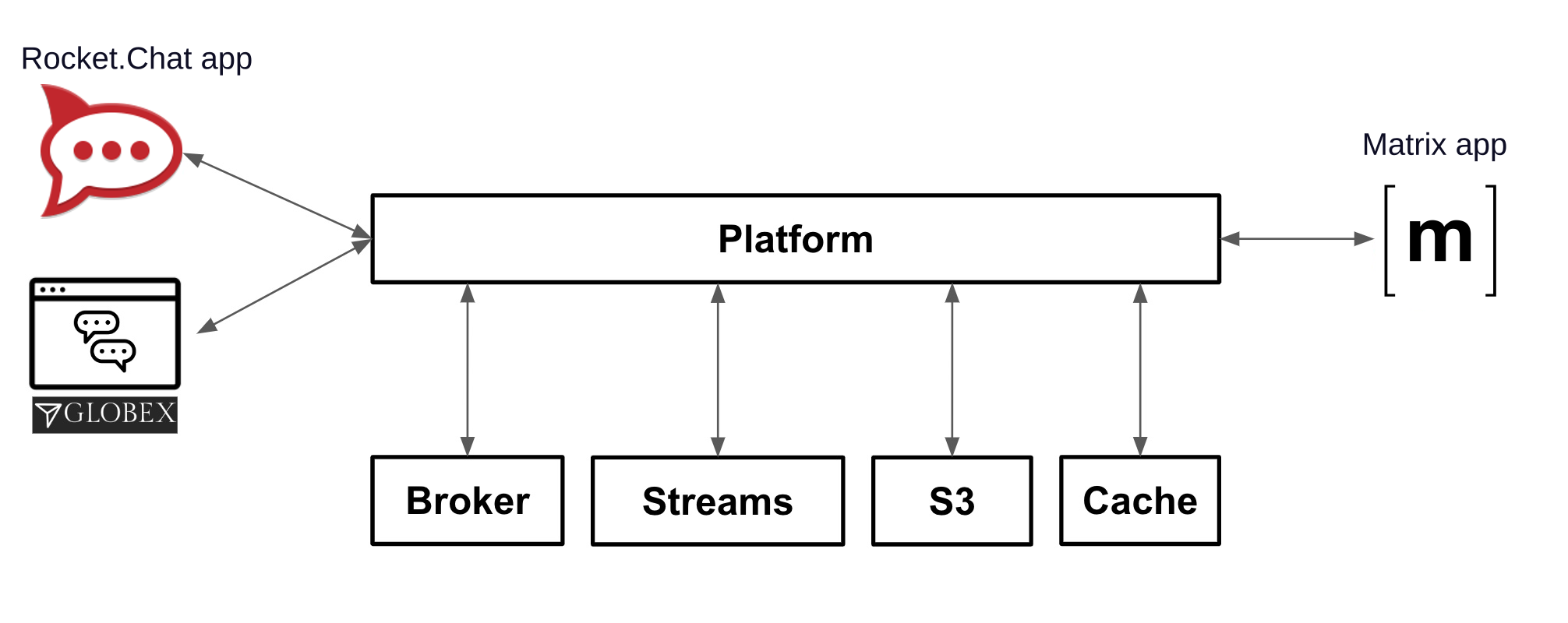
You will be involved in the new hub’s first implementation iteration (by completing all the module exercises). You will integrate two distinct customer facing platforms (left in the diagram, Rocket.Chat and Globex), with the agent’s channel (right in the diagram, Matrix).
Rocket.Chat and Matrix are open-source implementations of direct messaging platforms. While not as popular or ubiquitous as Slack or Discord, they can be installed on an OpenShift cluster and do not require registration, making them more suitable for a lab environment.
Customers (left) can choose to contact Globex via its Web portal or via a channel in Rocket.Chat, available on-line (using a browser). At the other end of the line, the team of agents (right) providing support services for Globex will use Matrix as their communication platform.
Module exercises
As per the picture below, this module is divided in 3 main activities:
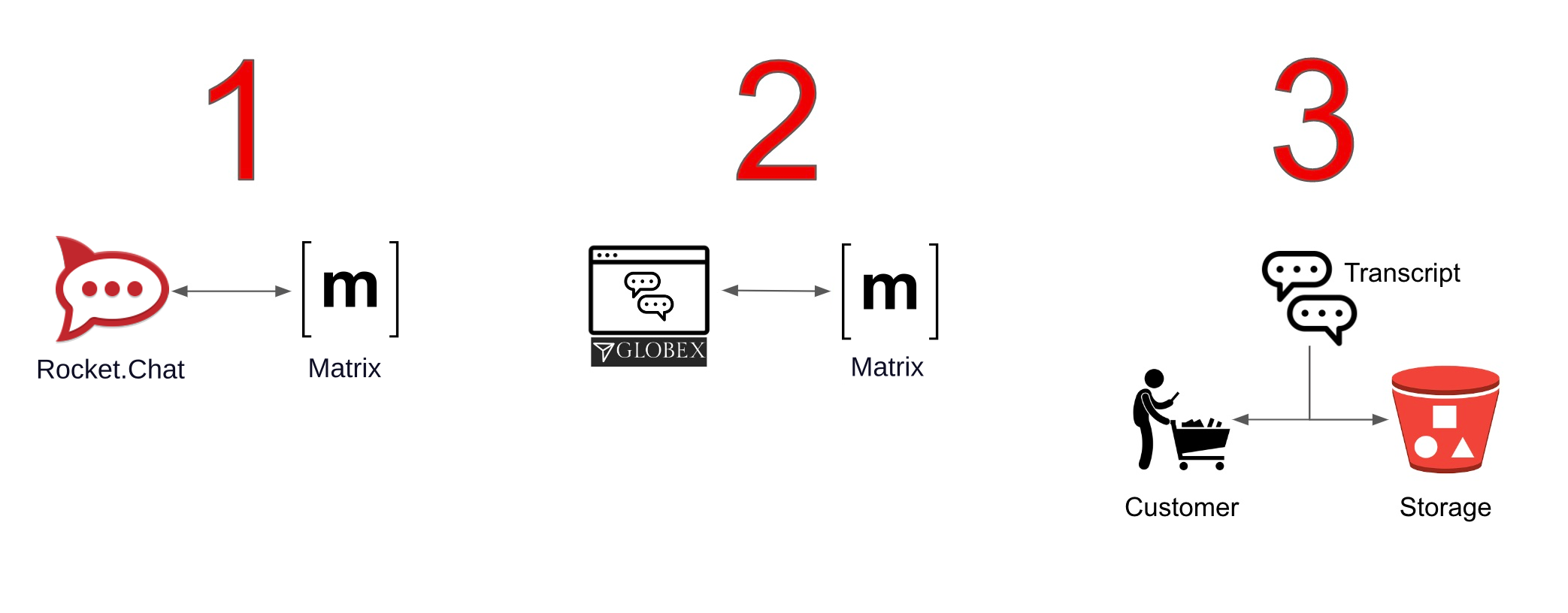
-
The first one integrates Rocket.Chat with Matrix.
Because the traffic (flow of messages) is bidirectional, you’ll need to-
Send messages from customers (in Rocket.Chat) to agents (in Matrix)
-
Send messages from agents (in Matrix) to customers (in Rocket.Chat)
-
-
The second activity, that showcases the platform’s open architecture, plugs in the Globex portal (Chat functionality), thus automatically enabling the Globex <-> Matrix message flow.
-
The third activity collects the conversation history (transcript), persists it in storage (S3 buckets) and shares access with customers as a file download.