Event Streams processing
1. Process event streams with Kafka Streams
Debezium produces a stream of data change events in one or more Kafka topics. In some cases the data in these topics need to be transformed, combined or aggregated before they can be consumed by target services.
In our use case for instance, the cashback service is interested in the total value of an order, not necessarily the value of each individual line item. However, The orders table in the Globex retail database does not contain the total value, as you can see in the entity relationship diagram.
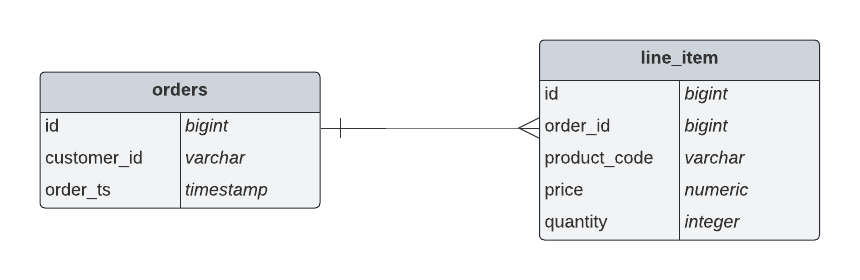
So we need to somehow combine the data change events streams from the orders table with the stream of the line_items table to obtain the total value for each order.
This is where stream processing libraries or frameworks come in. Libraries like Kafka Streams or Apache Flink allow to process streams of data consumed from a Kafka cluster in a continuous fashion. The result of the processing is typically stored in topics on the Kafka cluster. Processing capabilities can be stateless or stateful. Stateless processing include data transformations, filtering, mapping and so on. Stateful operations include aggregations and joins.
The processing logic of a Kafka Streams application is defined in a topology, which forms a graph of stream processors, where each processor represents a processing step in the processing topology. Kafka Streams comes with a Domain Specific Language (DSL) to define the topology in Java.
If you are familiar with SQL, a topology is quite similar to a set of SQL queries, but then applied on a stream of data rather then on static tables.
The order-aggregator service uses Kafka Streams to calculate the total value of an order out of the data change events of the orders and line_items tables. The topology does the following:
-
Consumes from the globex.updates.public.orders and globex.updates.public.line_item topics.
-
Joins the LineItem events with the Order events by Order ID. This produces a new stream of events which contain both the Order and the LineItem.
-
Groups the joined stream by Order ID
-
Aggregates the joined stream to produce a stream of AggregatedOrder events. The aggregation function adds the value of each individual line item to the total order value.
-
Publishes the aggregated order events in a Kafka topic, in this case the globex.order-aggregated topic.
In case you want to see how this looks like in code, click on the link below:
Click to see the code
public Topology buildTopology() {
StreamsBuilder builder = new StreamsBuilder();
final Serde<Long> orderKeySerde = DebeziumSerdes.payloadJson(Long.class);
orderKeySerde.configure(Collections.emptyMap(), true);
final Serde<Order> orderSerde = DebeziumSerdes.payloadJson(Order.class);
orderSerde.configure(Collections.singletonMap(JsonSerdeConfig.FROM_FIELD.name(), "after"), false);
final Serde<Long> lineItemKeySerde = DebeziumSerdes.payloadJson(Long.class);
lineItemKeySerde.configure(Collections.emptyMap(), true);
final Serde<LineItem> lineItemSerde = DebeziumSerdes.payloadJson(LineItem.class);
lineItemSerde.configure(Collections.singletonMap(JsonSerdeConfig.FROM_FIELD.name(), "after"), false);
final Serde<OrderAndLineItem> orderAndLineItemSerde = new ObjectMapperSerde<>(OrderAndLineItem.class);
final Serde<AggregatedOrder> aggregatedOrderSerde = new ObjectMapperSerde<>(AggregatedOrder.class);
// KTable of Order events
KTable<Long, Order> orderTable = builder.table(orderChangeEventTopic, Consumed.with(orderKeySerde, orderSerde));
// KTable of Lineitem events
KTable<Long, LineItem> lineItemTable = builder.table(lineItemChangeEventTopic, Consumed.with(lineItemKeySerde, lineItemSerde));
// Join LineItem events with Order events by foreign key, aggregate Linetem price in Order
KTable<Long, AggregatedOrder> aggregatedOrders = lineItemTable
.join(orderTable, LineItem::getOrderId, (lineItem, order) -> new OrderAndLineItem(order, lineItem),
Materialized.with(Serdes.Long(), orderAndLineItemSerde))
.groupBy((key, value) -> KeyValue.pair(value.getOrder().getOrderId(), value),
Grouped.with(Serdes.Long(), orderAndLineItemSerde))
.aggregate(AggregatedOrder::new, (key, value, aggregate) -> aggregate.addLineItem(value),
(key, value, aggregate) -> aggregate.removeLineItem(value),
Materialized.with(Serdes.Long(), aggregatedOrderSerde));
aggregatedOrders.toStream().to(aggregatedOrderTopic, Produced.with(Serdes.Long(), aggregatedOrderSerde));
Topology topology = builder.build();
LOGGER.debug(topology.describe().toString());
return topology;
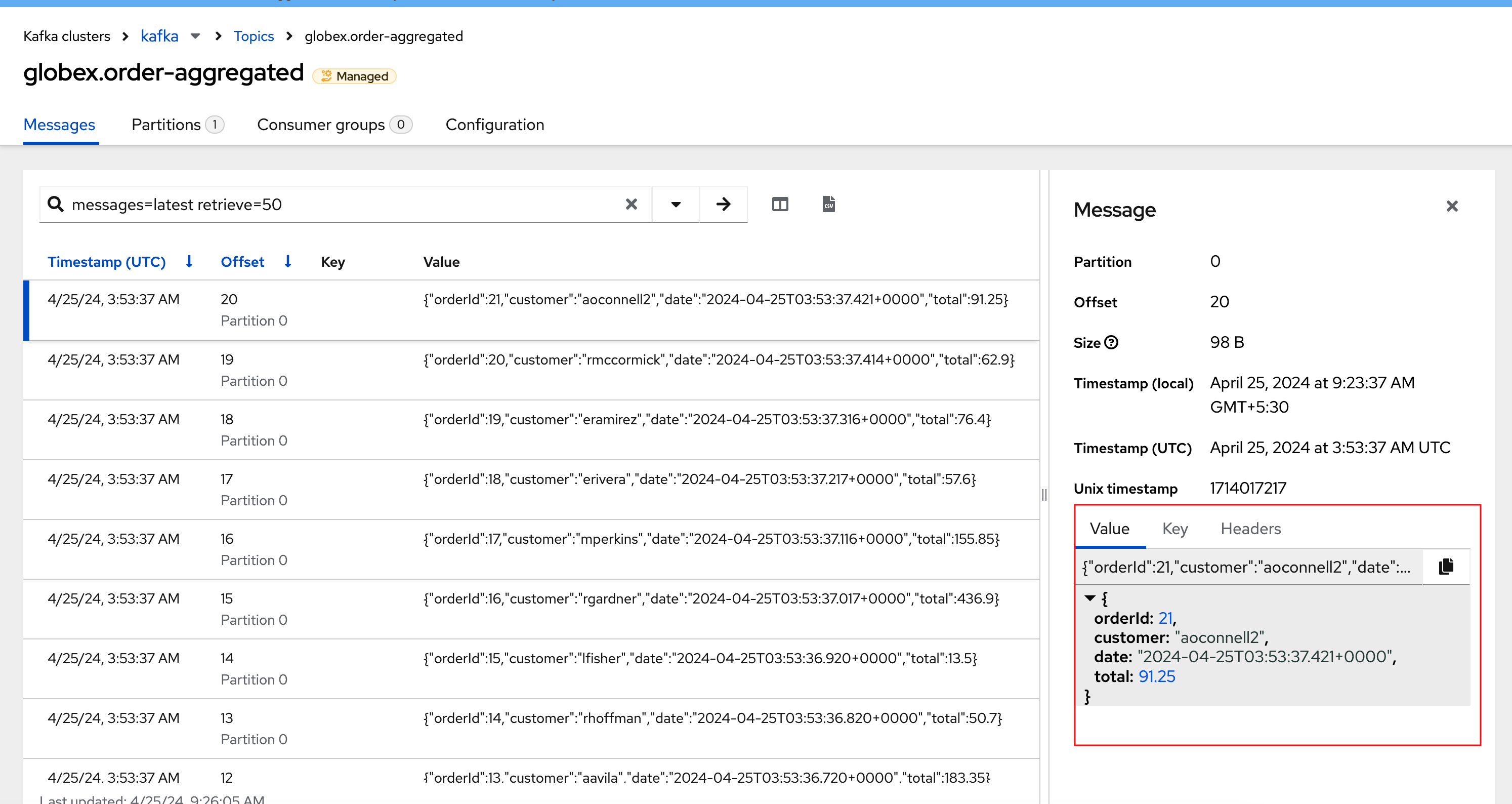
You can see the result of the streaming processing by inspecting the contents of the globex.order-aggregated topic in streams for Apache Kafka console.
-
Open the browser tab pointing to the streams for Apache Kafka console. If you have closed the tab, navigate to streams for Apache Kafka console.
-
From the Topics page, open the globex.order-aggregated topic, and verify that the topic contains one or more messages (the exact number depends on how many orders were created in the previous paragraph).
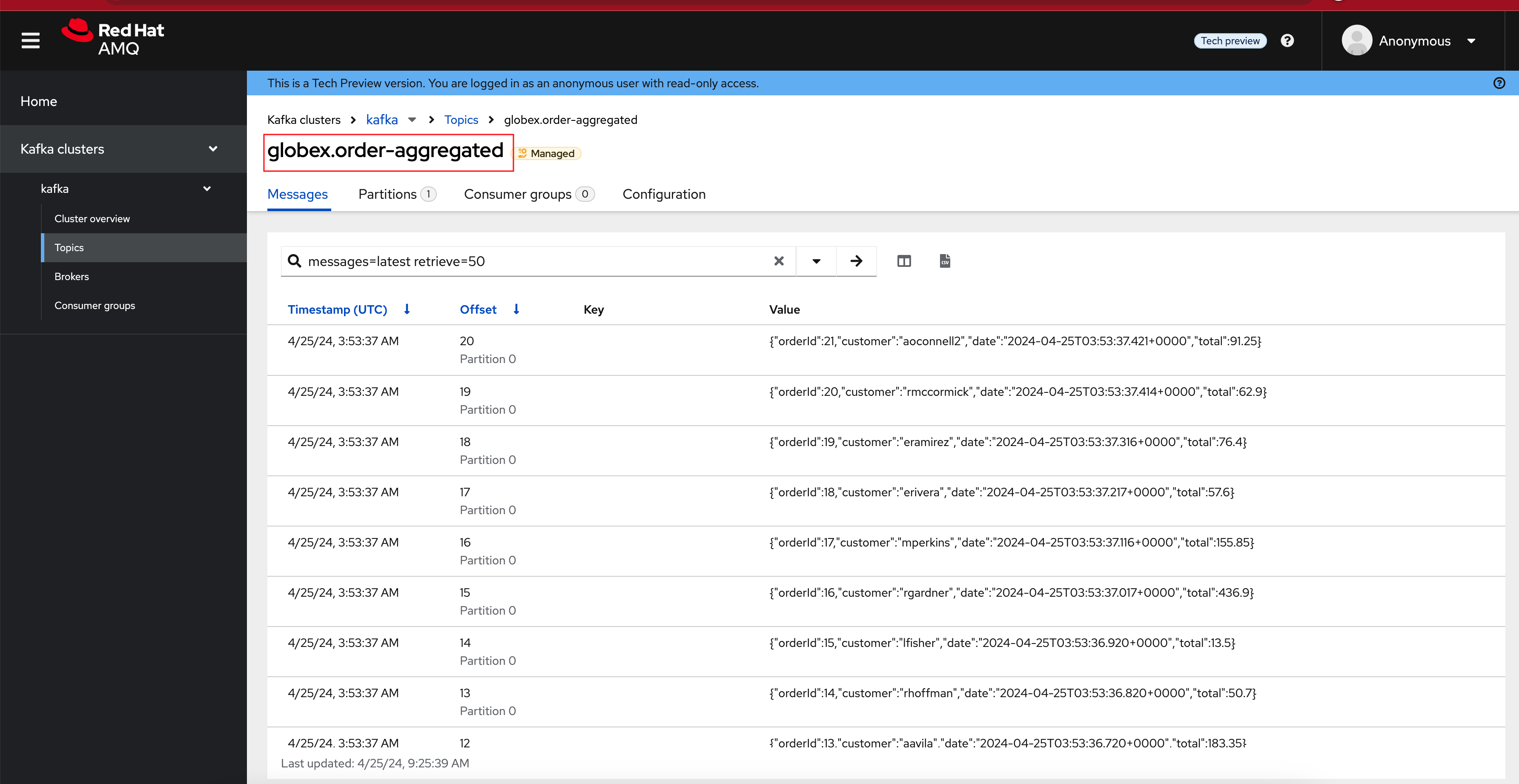
-
Expand the contents of a message. You should see a JSON structure which contains the order ID, the customer ID, the order creation date and the total value of the order.