Technical environment
Cluster details
-
All the activities for this workshop will be done on a shared OpenShift cluster.
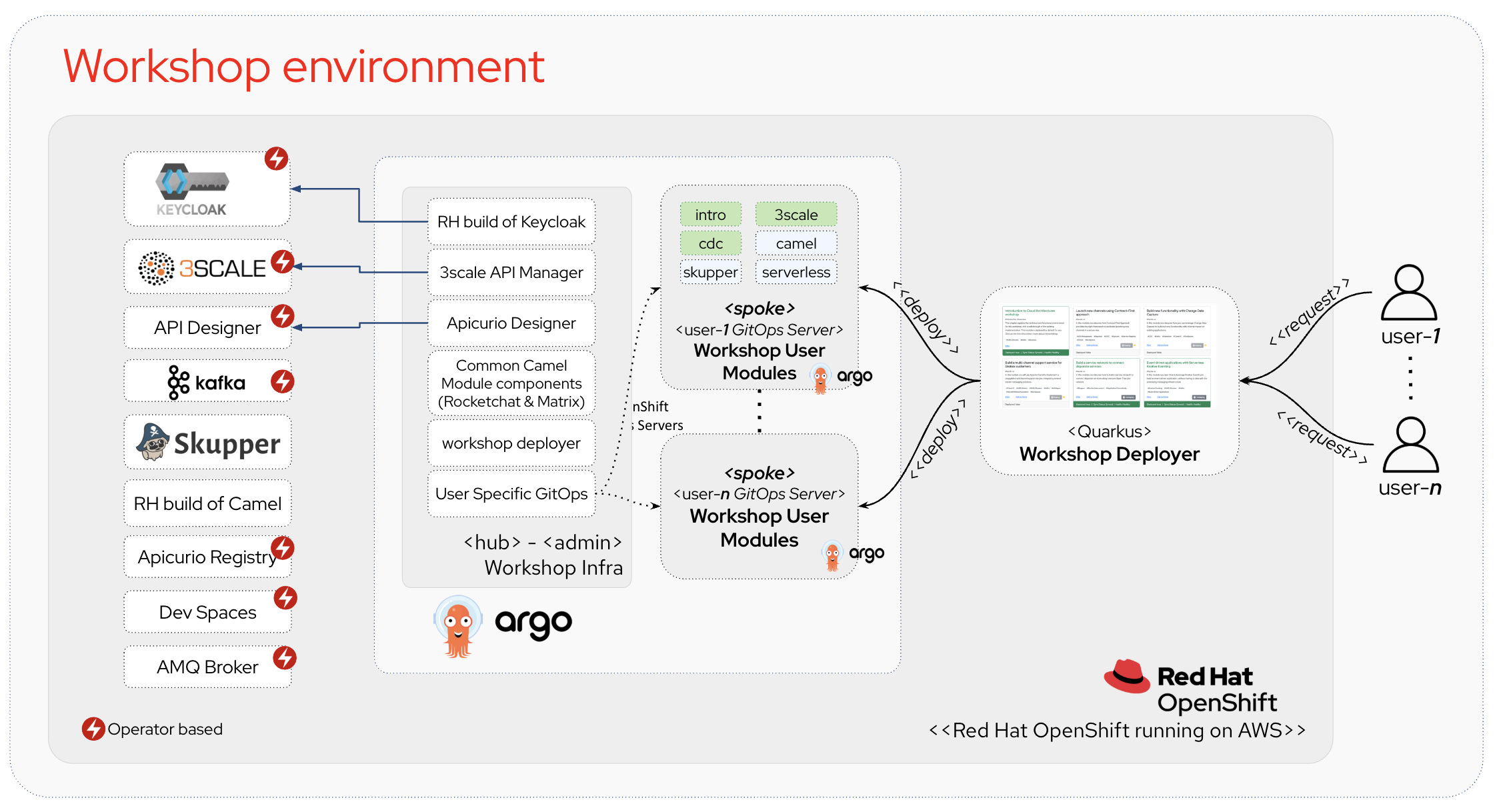 Figure 1. Workshop environment
Figure 1. Workshop environment -
Depending on the workshop modules you will be guided through, there are helper components such as Streams for Apache Kafka Console, an integrated development environment (IDE) called OpenShift Dev Spaces, based on Eclipse Che and some more.
-
All of these (including the IDE) are hosted on OpenShift as shown in Figure 1 above. These additional components will be introduced in the following chapters and workshop modules, where applicable.
-
We leverage OpenShift GitOps (aka ArgoCD) to manage the deployment of the workshop assets, in a hub and spoke model: a central ArgoCD (show as hub) instance which manages common assets and namespace-scoped ArgoCD (shown as spoke) instances which manage the per-user assets.
-
In total ArgoCD manages 350 applications per cluster, which represent more than 2500 pods and numerous secrets, configmaps and so on.
-
If you are interested to know more about this setup, click on the link below, or come to talk to the workshop instructors.
Details on the OpenShift GitOps setup
As mentioned before, we use a hub and spoke model to manage the workshop assets. A cluster-wide ArgoCD instance (hub) manages a number of namespace scoped ArgoCD (spoke) instances (1 per workshop user). These namespace scoped ArgoCD instances manage the workshop assets for a user.
You can log into your namespace scoped ArgoCD instance and have a look at the assets managed by the instance:
-
Navigate to ArgoCD. Expect to see the landing page of ArgoCD.
-
Click on the Log in via OpenShift link, and log in with your OpenShift credentials ({user_name}/{user_password}).

-
If this is the first time you access the ArgoCD console, you have to authorize ArgoCD to access your account. In the Authorize Access window click on Allow selected permissions.
-
You are redirected to the application overview page of ArgoCD, which shows you all the applications that this instance of ArgoCD is managing. In ArgoCD language, an application represents a collection of Kubernetes/OpenShift resources that are managed as a whole.
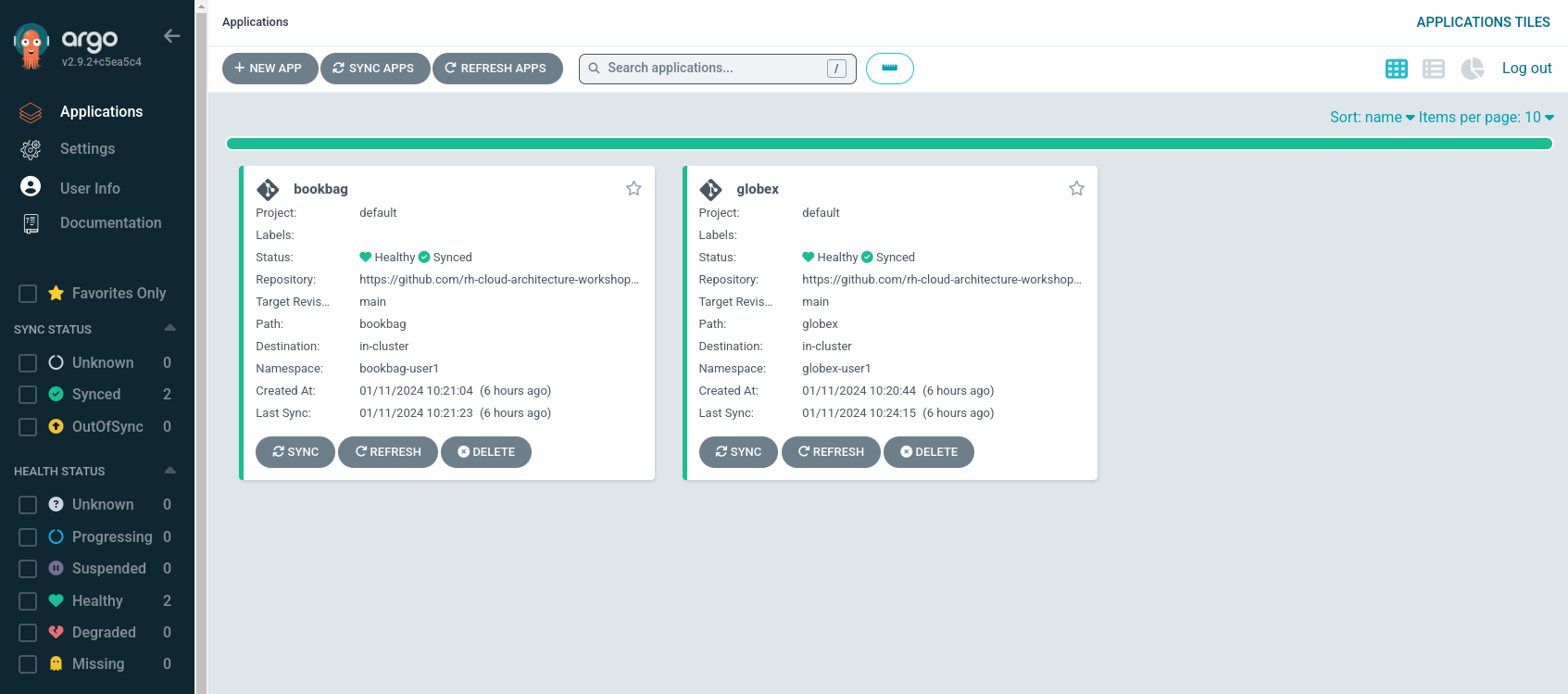
The list of applications managed by the ArgoCD instance depends on which modules you have deployed. -
If you click on one of the application cards, you’ll see an overview of all the Kubernetes resources managed as part of the application. This is for example an partial view of the Globex application:
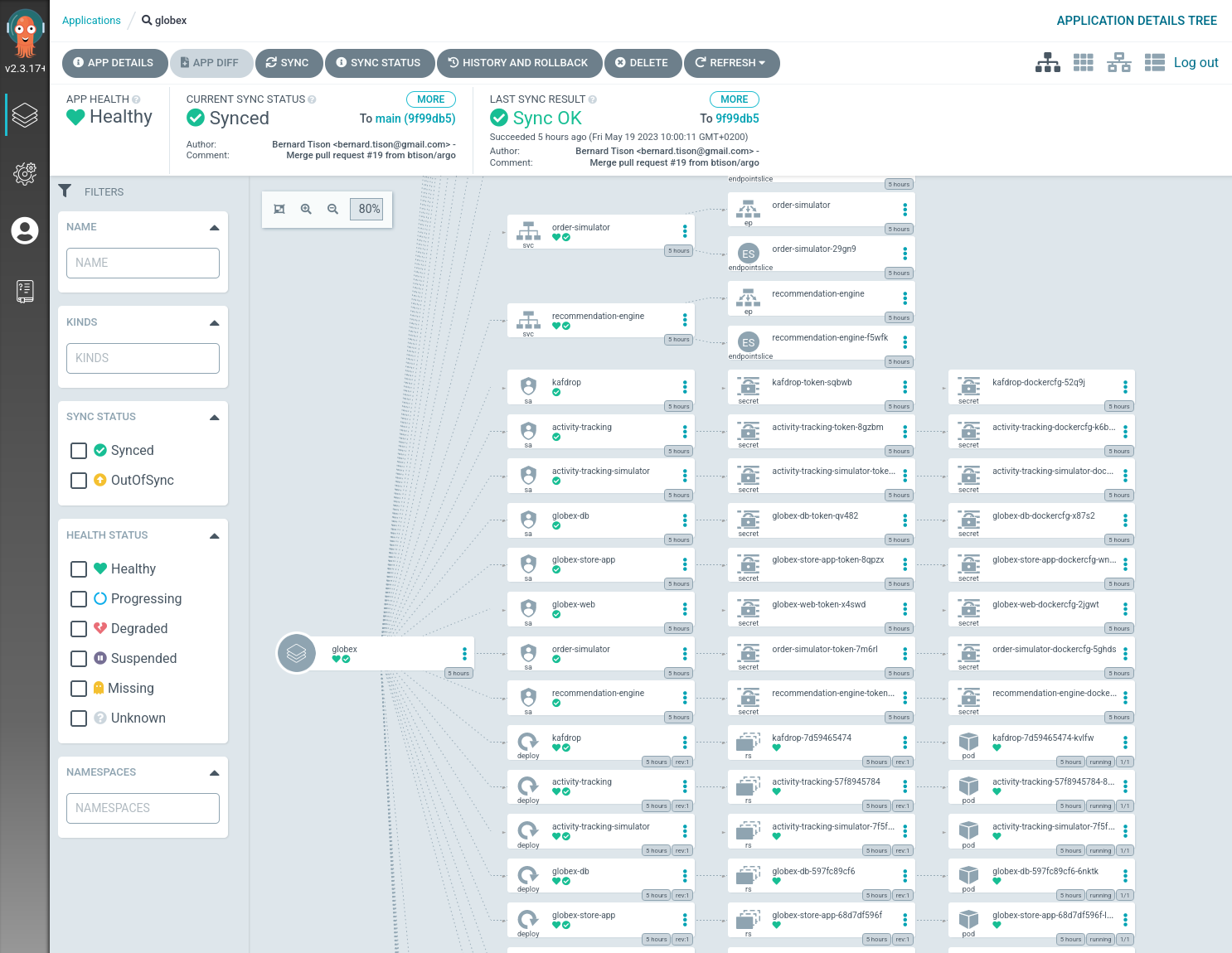
-
The way ArgoCD works is that the desired state of an application is described in a manifest, which is hosted in a version control system. ArgoCD makes sure that the deployed state of the application matches the desired state as described in the manifest. Changes in the manifest (a new commit for example) are picked up by ArgoCD and applied. Hence the name GitOps, which itself is an evolution of Infrastructure as code.
| ArgoCD manifests can take many forms. For this workshop we opted for Helm charts. You can find the Helm charts for this workshop here. |